Building Security Checklist
This building security checklist article discusses actions you can take to protect your company, company assets and employees.
Your work location may have physical security safeguards, but security measures work best when supported by your employees. You can significantly reduce the vulnerability of the company, co-workers, customers, and yourself by complying with this building security checklist.
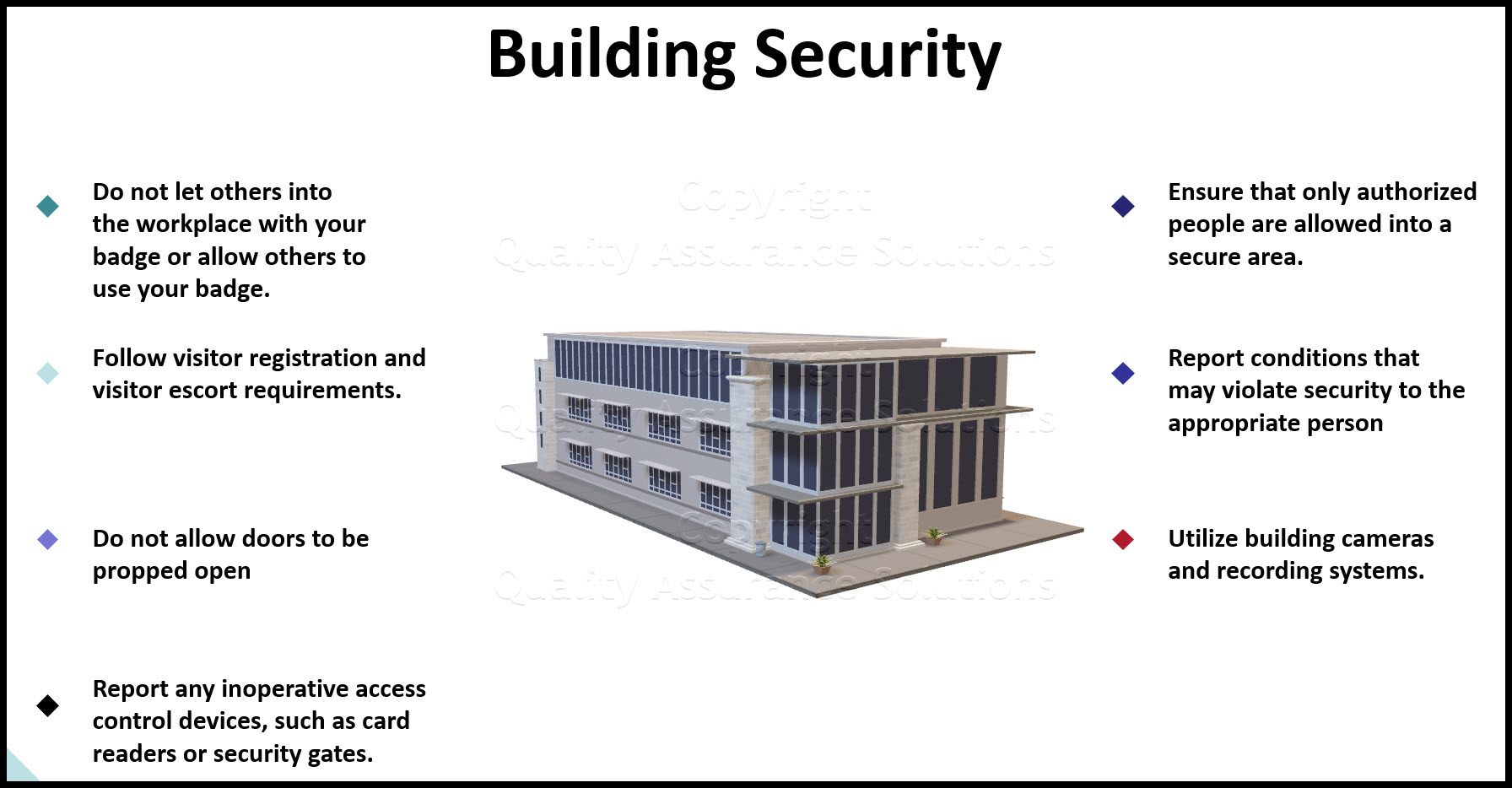
- Do not let others into the workplace with your badge or allow others to use your badge.
- Follow visitor registration and visitor escort requirements.
- Do not allow doors to be propped open
- Report any inoperative access control devices, such as card readers or security gates.
- Ensure that only authorized people are allowed into a secure area.
- Report conditions that may violate security to the appropriate Physical Security office or your manager.
- Utilize building cameras and recording systems.
- Consider professional security companies.
You are not being discourteous when you ask to see someone's ID. Instead, you assist in the protection of employees as well as the company's and its customers' information. Those questioned should see the value in maintaining a secured environment.
TrainingKeeper Software. Keep, organize and plan all your employees' training and activities. Software includes multi-user support with reports, certs, and calendars.
Building Security Checklist Includes Limiting Access
How many times have you allowed unidentified persons to follow you into your place of business without asking them for proper identification?
Restricting building access is our first line of defense for keeping intruders and thieves out of our facilities. Building access control is the initial barrier against equipment and information theft / loss from our work environment.

A second line of defense, should intruders gain access, is the physical location of our computers or other valuable equipment. Equipment such as file servers and similar devices should be located in additionally secured areas within our facilities. We should also use anti-theft products to help protect our computer / valuable equipment and valuable information, e.g., cabling that connects the equipment to a desk, beam, or other anchor; strong adhesives; battery-powered alarm system; etc.
One should question unfamiliar persons before allowing them access to our facilities, and notify security of unidentified personnel carrying equipment out the door. It doesn't do us much good to protect our computers from intruders and thieves with passwords and antivirus software, when at the same time, we're holding the door open for them.
Employee Handbook Kit includes two Employee Handbook templates for Professional & Manufacturing. Includes over 60 policies and benefits templates.
Social Engineering
Don't forget to consider Social Engineering for your building security checklist.
Today, corporations also need to be concerned about a different kind of access vulnerability. "Social Engineering" refers to the various methods used to gain unauthorized access to corporate assets, such as computer networks and telephone systems.
These pretenders are no ordinary computer hackers, working cloak and dagger. Instead, they work in the open, acting friendly and polite as they request information from you. The intruder may claim to be an employee who has lost his/her password and needs you to provide system access to help solve an urgent problem.
Others may pose as local telephone technicians who, under the pretext of testing the system, request that you transfer them to an outside line. The following information will help you recognize the characteristics of social engineering so that you don't become a victim:
- Telephone calls are the most common social engineering technique. They are quick and can be used to easily impersonate almost anyone.
- One of the most renowned hackers of all time did most of his work through social engineering, such as scamming telephone agents for access codes. Only 15 percent of his work was done on a computer.
- Beware of anyone requesting a password, account, personal information, or system access without proper authorization and identification.
- Male hackers often use "voice changers" to imitate females when requesting information over the telephone.
- Use your instincts and be observant. If you're unsure of a person's identity, do not give out any sensitive information. Request and verify information concerning their identity and call them back.
Remember, each one of us has a responsibility for safeguarding the information and equipment within our work environment.
- QAS Home
- Building Security
|
Quality Assurance Solutions Robert Broughton (805) 419-3344 USA |
 |
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications | ||
|
450+ Editable Slides with support links | ||
|
Corrective Action Software | ||
|
Plan and Track Training | ||
|
AQL Inspection Software |
|
Learn and Train TRIZ | ||
|
Editable Template | ||
|
Templates, Guides, QA Manual, Audit Checklists | ||
|
EMS Manual, Procedures, Forms, Examples, Audits, Videos | ||
|
On-Line Accredited Certifications Six Sigma, Risk Management, SCRUM | ||
|
Software, Videos, Manuals, On-Line Certifications |